
There are basically two ways an electric car can be charged: ‘Slow’ charging or ‘fast’ charging’. These two different charging methods are differentiated mainly by how quickly they can charge your electric car. Electric cars can be charged by both AC and DC charging sources with each method having its advantages and disadvantages depending on what your needs are. Knowing these can help you make the best choices when deciding how to charge.
What Is AC Charging?
AC stands for Alternating Current, which means that the current changes direction periodically. The most common type of AC is the one that has a frequency of 50Hz (50 cycles per second) in Australia and most other parts of the world. This type of current is used in most homes and buildings to power lights, appliances, and other devices.
One of the main differences between AC and DC electricity is that AC can be transmitted over long distances with less loss of energy than DC. This is why AC is typically used for power transmission from power plants to homes and buildings
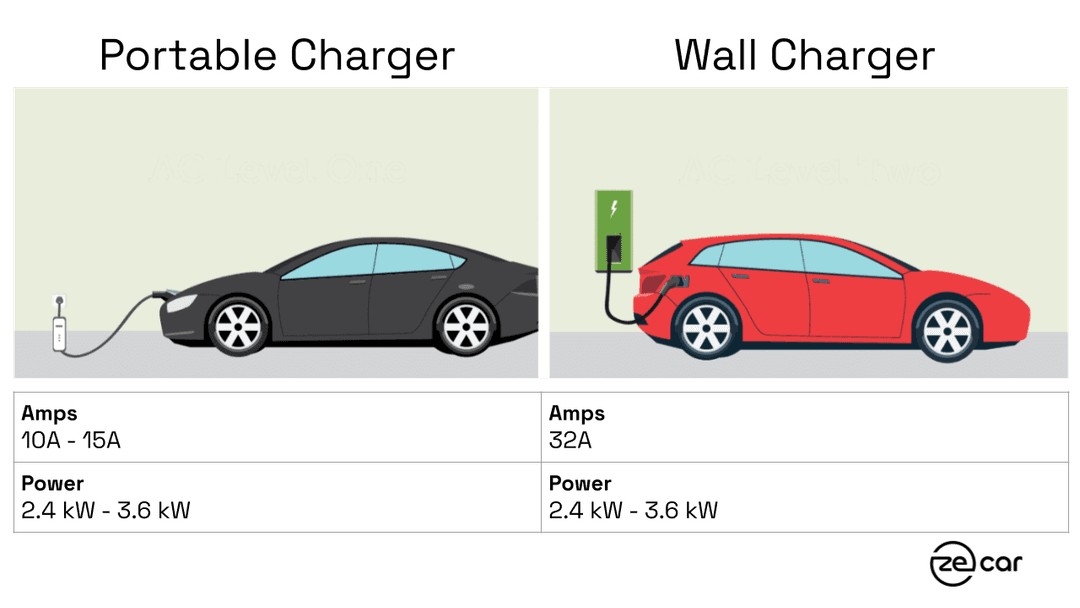
AC charging is the most common type of charging and is often referred to as "level 1" or "level 2" charging. Level 1 charging uses a standard 240-volt household outlet and a portable charger and can take up to 30 hours to fully charge a car. Level 2 charging uses a dedicated circuit via a wall charger and can take as little as 4-6 hours to fully charge a car. AC charging is more convenient because it can be done at home and can be used with any electric car
What Is DC Charging?

DC stands for Direct Current, which means that the current flows in one direction. DC electricity is used in batteries, electronic devices, and vehicles such as electric cars and is better for shorter distances and charging batteries.
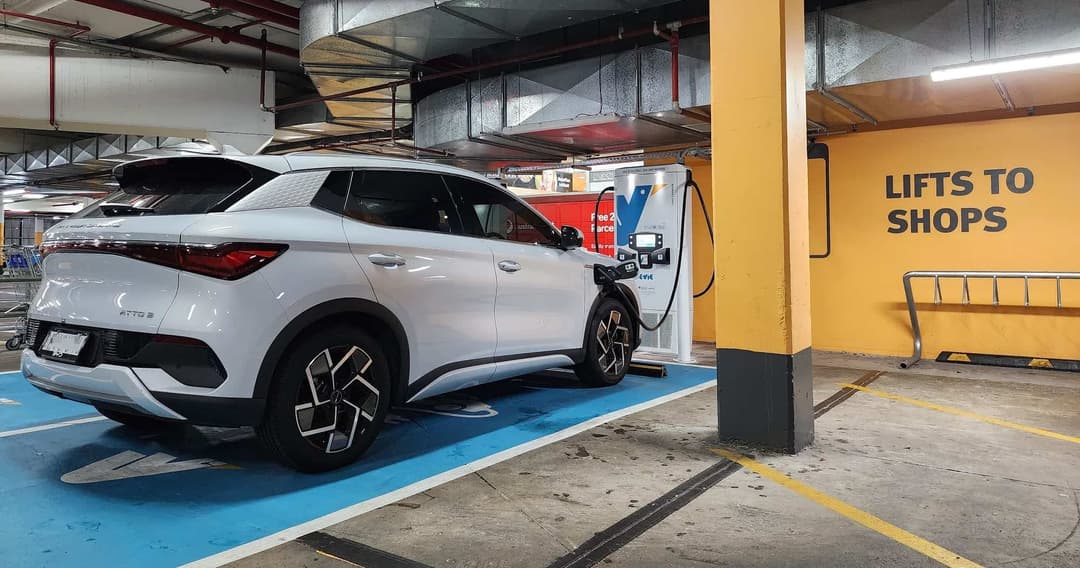
DC charging, also known as "level 3" or "fast charging," uses a higher voltage and can charge a car much faster than AC charging. It can take as little as 30 minutes to an hour to fully charge a car. DC charging stations are typically located at public charging stations, such as at shopping centers, rest areas, and service stations.
AC Charging Pros & Cons
AC Charging Pros
The main advantages of AC charging is its widespread availability, convenience and lower cost. It can be done using a standard outlet found in most homes.
AC Charging Cons
The main disadvantage of AC charging is that it is typically slower than DC charging. AC charging typically provides a charging rate of 3-6 kW. In contrast, DC charging, also known as Level 3 or fast charging can provide a charging rate of 50-150 kilowatts or more. As a result, an EV charged using Level 2 charging will take longer to charge than one charged using Level 3 DC fast charging. This can be an inconvenience for EV owners who need to charge their vehicle quickly and may limit the distance they can travel before needing to charge again.
DC Charging Pros & Cons
DC Charging Pros
One of the main advantages of DC fast charging is its speed, making it a convenient option for long distance travel. Additionally, DC fast charging can also be used to extend the range of an EV in a short amount of time. As you can see from the table below, DC Charging provides 100km of range significantly faster than AC charging.
DC Charging Cons
DC fast charging can also have some downsides. One is that it generates more heat, which can cause wear and tear on the battery and its components over time. Additionally, not all EVs are compatible with DC fast charging, so it's important to check the capabilities of your specific vehicle.
AC vs. DC Charging Bottom Line
In summary, AC charging is the most common type of charging and is typically done at home using a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station. DC fast charging is typically done at designated fast charging stations, such as those found at public charging networks, and is often more expensive than AC charging. Each type of charging has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it's important to consider your charging needs and the capabilities of your specific EV when deciding which type of charging to use.
Stay up to date with the latest EV news
- Get the latest news and update
- New EV model releases
- Get money savings-deal
